Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease By Best Neurologist Dr Abhinav Gupta
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease is a complex and devastating condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. As healthcare professionals, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of this disease in order to provide the best possible care and support to patients and their families..
2. What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
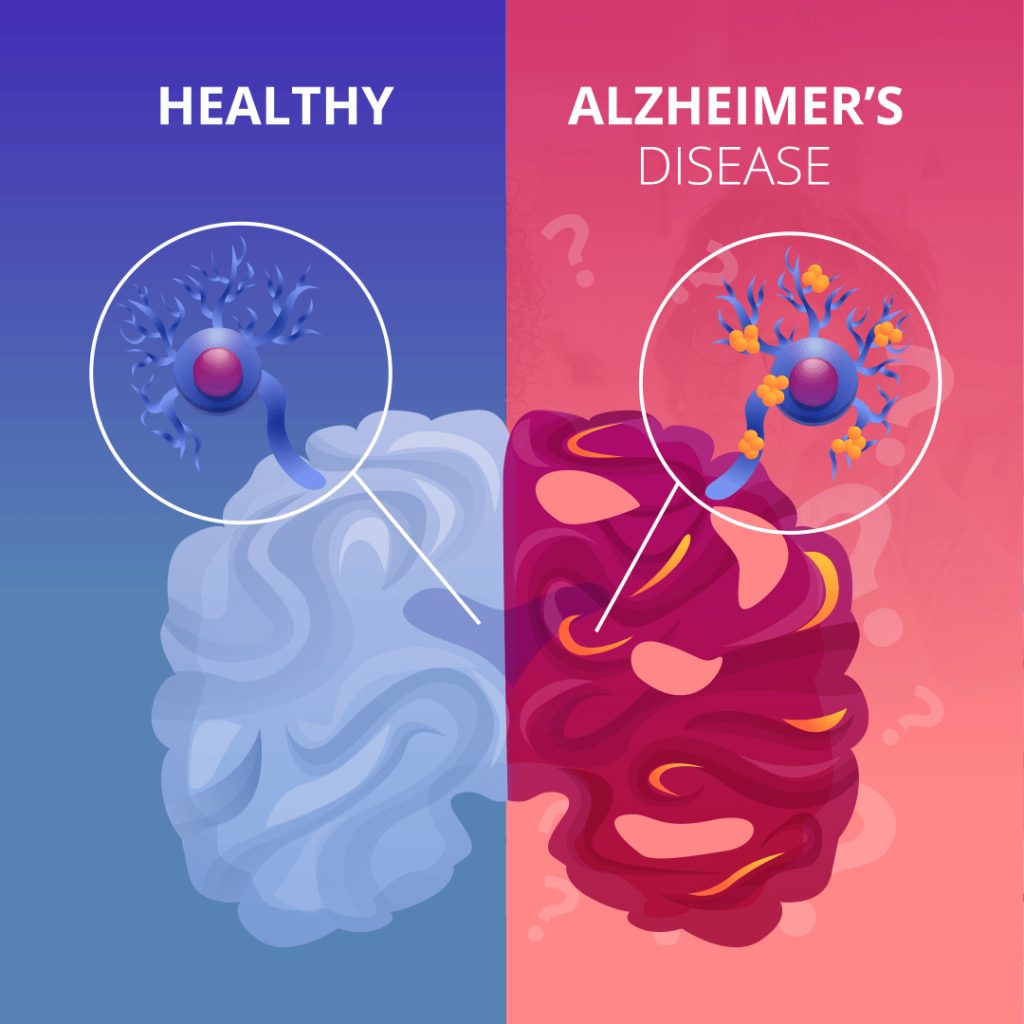
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for approximately 60-80% of all cases. This debilitating condition primarily affects older adults and gradually worsens over time.
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still unknown, although researchers believe it may be a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. In Alzheimer’s disease, abnormal deposits of proteins form plaques and tangles in the brain, interfering with the communication between brain cells and ultimately causing their death.
Early symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease often include mild forgetfulness and difficulty with problem-solving and language. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience confusion, disorientation, personality changes, and difficulty performing daily tasks.
While there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include medications to slow down the progression of the disease, behavior and lifestyle interventions, and supportive therapies such as cognitive rehabilitation.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the causes and risk factors associated with Alzheimer’s disease, shedding light on the latest research and advancements in understanding this complex condition. Stay tuned for more valuable insights into the world of Alzheimer’s disease!
3. Recognizing the signs and symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for timely intervention and support. While the earliest stages of the disease may present with subtle changes in memory and cognitive function, it is important for healthcare professionals to be vigilant in identifying these early warning signs.
Common signs of Alzheimer’s disease include frequent forgetfulness, difficulty with problem-solving and decision-making, confusion in familiar environments, changes in personality and mood, and struggles with language and communication. These symptoms may also be accompanied by difficulty in completing familiar tasks and a general decline in cognitive abilities.
By being aware of these indicators, healthcare professionals can facilitate early diagnosis and intervention, allowing for better management of the disease and improved quality of life for patients and their families. In the next section, we will explore the diagnostic process for Alzheimer’s disease, including the various assessment tools and techniques that healthcare professionals can utilize to accurately identify and evaluate the condition. Stay tuned for an informative discussion on this crucial aspect of Alzheimer’s disease management.
4. Diagnosing Alzheimer’s Disease
In diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, healthcare professionals utilize a combination of assessments and evaluations to accurately identify the condition. The process typically begins with a thorough medical history review and physical examination to rule out other potential causes of cognitive decline.
One commonly used assessment tool is the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), which evaluates cognitive function in areas such as memory, attention, and language. Another valuable tool is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which assesses various cognitive domains including executive function, attention, and visuospatial abilities.
In addition to these standardized tests, healthcare professionals may also consider brain imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET) scans to assess brain structure and function. These imaging studies can help to identify changes in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
By incorporating a comprehensive diagnostic approach, healthcare professionals can provide accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. In the following section, we will explore the available treatment options and management strategies that can help improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition. Stay tuned for further practical insights into Alzheimer’s disease care.
5. Treatment options for Alzheimer’s Disease
Once a healthcare professional has accurately diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease, it is crucial to develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs. While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, various treatment approaches can help alleviate symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease.
Pharmacological interventions are often used in the management of Alzheimer’s. Cholinesterase inhibitors, such as donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine, are commonly prescribed to improve cognitive function and help with memory loss. Another medication called memantine may also be used to regulate glutamate levels in the brain, which can help slow down cognitive decline.
Non-pharmacological interventions are equally important and can include cognitive stimulation therapy, physical exercise, and occupational therapy. These approaches aim to enhance overall brain health, promote social interaction, and maintain independence for as long as possible.
In the next blog section, we will explore these treatment options in more detail and discuss their efficacy and potential side effects. Understanding the available treatments can empower healthcare professionals to provide the best care and support to individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease.
6. Providing care and support for individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease
Next section: Providing care and support for individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease
Caring for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease requires a compassionate and personalized approach. In addition to medical treatment, healthcare professionals play a crucial role in providing emotional support and guidance to both patients and their families.
Creating a safe and comfortable environment is essential for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Simple modifications such as installing handrails, removing clutter, and labeling important items can prevent falls and promote independent living. It is equally important to encourage a regular routine and provide supervision as needed.
Effective communication strategies are essential when caring for individuals with Alzheimer’s. Using clear, concise language and non-verbal cues can help facilitate understanding, while maintaining a calm and patient demeanor. Active listening and validation of emotions are also crucial in fostering trust and maintaining a positive relationship.
Educating families about the disease’s progression and common challenges can alleviate anxiety and provide realistic expectations. Offering support groups, counseling, and connecting families with local resources can help them navigate the emotional and logistical aspects of caregiving.
In the following blog section, we will delve deeper into the strategies and resources available to healthcare professionals for providing comprehensive care and support to individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their families.
7. The role of healthcare professionals in Alzheimer’s Disease management
In the previous blog section, we discussed the importance of providing care and support for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Now, let’s further explore the role of healthcare professionals in the management of this condition.
Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and care providers, play a vital role in the overall management of Alzheimer’s disease. They are responsible for diagnosing the condition, developing a comprehensive care plan, and monitoring the progress of the patient.
One of the crucial tasks healthcare professionals perform is medication management. Alzheimer’s disease often requires the use of medication to manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Healthcare professionals prescribe appropriate medications, monitor their effectiveness, and adjust the dosage as needed.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals educate caregivers and family members about the disease and its management. They provide guidance on how to handle challenging behaviors, communicate effectively, and ensure the safety and well-being of the individual with Alzheimer’s.
In the next blog section, we will discuss in detail the various responsibilities of healthcare professionals in the management of Alzheimer’s disease, including specific interventions and resources available to them. Stay tuned for insightful information that will support your practice as a healthcare professional in caring for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
8. Research and advancements in Alzheimer’s Disease
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in research and advancements in the field of Alzheimer’s disease. These developments have paved the way for a better understanding of the condition, improved diagnostic tools, and more effective treatment options.
Researchers have been studying the underlying causes of Alzheimer’s disease, including the role of genetics, lifestyle factors, and the buildup of abnormal proteins in the brain. By uncovering these mechanisms, healthcare professionals can develop more targeted interventions and therapies.
Advancements in diagnostic tools have also made it easier to identify Alzheimer’s disease in its early stages. New technologies, such as brain imaging and biomarker tests, can detect the presence of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, the hallmark signs of Alzheimer’s, even before symptoms appear. This early detection allows for earlier intervention and better outcomes for patients.
In terms of treatment, there have been significant advancements in medication options. While there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, there are medications available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with the condition. Healthcare professionals now have a range of options to choose from, including cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine, depending on the needs and stage of the disease.
In addition to medication, non-pharmacological interventions have also shown promise in managing Alzheimer’s disease. These interventions include cognitive stimulation therapy, reminiscence therapy, and physical exercise, among others. Healthcare professionals have a crucial role in implementing and monitoring these interventions to ensure their effectiveness.
Furthermore, research has led to the development of specialized care facilities and resources to support individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their caregivers. Memory care units and Alzheimer’s clinics provide a supportive and safe environment for individuals with the disease, offering specialized care and programs tailored to their unique needs. Healthcare professionals can refer patients and caregivers to these resources, ensuring they receive the best possible care and support.
As healthcare professionals, it is essential to stay updated on the latest research and advancements in Alzheimer’s disease. By doing so, we can provide our patients with the most current and evidence-based care. In the next section, we will delve deeper into these research findings and advancements, exploring their implications for healthcare professionals in the management of Alzheimer’s disease.
Stay tuned for an insightful discussion on how these research and advancements can enhance your practice and improve outcomes for individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease.
9. Conclusion: Promoting awareness and understanding of Alzheimer’s Disease among healthcare professionals
Next section:
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the latest research and advancements in the field of Alzheimer’s disease. We have learned about the underlying causes of the condition, the importance of early detection, the range of medication options, and the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions.
As healthcare professionals, it is crucial to stay informed and up-to-date on these developments. By continuously expanding our knowledge, we can provide the best possible care for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in raising awareness and promoting understanding of this condition. By sharing our knowledge with colleagues, educating our patients, and advocating for resources and support, we can improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their caregivers.
Let us strive to be champions in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease by staying informed, supporting research, and offering compassionate care. Together, we can make a difference.